University certificate
Accreditation/Membership
.png)
The world's largest faculty of nursing”
Introduction to the Program
A comprehensive and 100% online program, exclusive to TECH, with an international perspective supported by our membership with The Society for Academic Specialists in General Obstetrics and Gynecology"
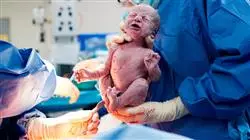
Today, many women choose to delay conception, which has increased the incidence of high-risk pregnancies, particularly in Western countries. Nevertheless, scientific advances and more comprehensive medical monitoring have contributed to favorable outcomes, ensuring maternal and infant well-being. In addition, pregnancy education programs and breastfeeding support initiatives have raised greater awareness among the population, promoting improved healthcare. In this context, the nursing specialist faces challenges that encompass not only the care of the pregnant woman but also that of the newborn.
With the aim of providing information based on the most recent scientific evidence, this program has been designed by a faculty team with expertise in Obstetrics at leading hospital centers. Graduates will have access to cutting-edge multimedia resources, enabling them to deepen their knowledge of essential areas such as preconception consultation, prenatal care, pregnancy monitoring, maternal nutrition, labor and delivery, and postpartum care. Furthermore, clinical case simulations will serve as a key tool for the direct application of knowledge in professional practice, enhancing the ability to respond effectively to real-world situations.
This fully online program offers flexible study options, adapting to the needs of each student. With access to the virtual platform from any device, professionals will be able to organize their coursework according to their personal and professional responsibilities, ensuring high-quality training without compromising their daily practice.
Thanks to the collaboration with The Society for Academic Specialists in General Obstetrics and Gynecology (SASGOG), students will gain access to a national network of experts, share best practices, participate in women’s health initiatives, and strengthen their profile in the medical field. This alliance boosts their professional development, provides access to specialized resources, and consolidates their position within a community recognized for its excellence in academic obstetrics and gynecology.
You will acquire advanced competencies in the early detection and management of obstetric complications”
This Master's Degree in Obstetric Nursing contains the most complete and up-to-date scientific program on the market. The most important features include:
- The development of practical cases presented by experts in Obstetric Nursing
- The graphic, schematic, and practical contents with which they are created, provide scientific and practical information on the disciplines that are essential for professional practice
- Practical exercises where the self-assessment process can be carried out to improve learning
- Special emphasis on innovative methodologies in Obstetric Nursing
- Theoretical lessons, questions to the expert, debate forums on controversial topics, and individual reflection assignments
- Content that is accessible from any fixed or portable device with an internet connection
You will deepen your expertise in the use of digital tools in obstetric care, optimizing information management and neonatal follow-up”
The faculty includes professionals from the field of Obstetric Nursing, who bring to this program the value of their professional experience, along with renowned specialists from leading societies and prestigious universities.
The multimedia content, developed with the latest educational technology, will provide the professional with situated and contextual learning, i.e., a simulated environment that will provide an immersive learning experience designed to prepare for real-life situations.
This program is designed around Problem-Based Learning, whereby the student must try to solve the different professional practice situations that arise throughout the program. For this purpose, the professional will be assisted by an innovative interactive video system created by renowned and experienced experts.
You will apply regulations and bioethical principles in obstetric practice, ensuring the protection of maternal and child rights"
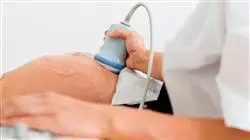
This program delves into the relevance of the nutrition of the pregnant woman and its future consequences on the baby"
Syllabus
TECH has designed a curriculum aimed at providing professionals with detailed and up-to-date knowledge on the care of pregnant women and newborns. This program, structured into 8 modules, covers everything from preconception consultation to neonatal care. In addition, it explores the anatomophysiological changes during pregnancy, including cardiovascular, metabolic, endocrine, and renal adaptations, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the gestational process and its impact on both mother and baby.

You will also delve into the physiology of breastfeeding, addressing milk secretion and the factors that may inhibit it”
Module 1. Preconception Consultation
1.1. Need for Preconception Consultation
1.2. Content of the Consultation
1.2.1. Medical History
1.2.2. Physical Examination
1.2.3. Complementary Tests
1.3. Health Education and Promotion
1.4. Pharmacological Supplementation
Module 2. Pregnancy
2.1. Duration of Pregnancy. Nomenclature
2.2. Anatomophysiological Modifications
2.2.1. Cardiovascular and Cardiac Changes
2.2.1.1. Cardiac Changes
2.2.1.2. Hematological Changes
2.2.1.3. Vascular Changes
2.2.2. Respiratory Changes
2.2.2.1. Anatomical Changes
2.2.2.2. Functional Changes
2.2.3. Renal and Urinary Changes
2.2.3.1. Anatomical Modifications
2.2.3.2. Functional Modifications
2.2.4. Metabolic Changes
2.2.4.1. Weight Gain
2.2.4.2. Basal Metabolism
2.2.4.3. Carbohydrate Metabolism
2.2.4.4. Lipid Metabolism
2.2.4.5. Protein Metabolism
2.2.4.6. Acid-Base Balance
2.2.4.7. Water Metabolism
2.2.4.8. Minerals and Vitamins
2.2.5. Genital and Mammary Changes
2.2.5.1. External Genitals
2.2.5.2. Internal Genitals
2.2.5.3. Breast Changes
2.2.6. Endocrine Changes
2.2.6.1. Constitution of the Fetoplacental Unit
2.2.6.2. Pituitary Gland
2.2.6.3. Thyroid
2.2.6.4. Parathyroid
2.2.6.5. Pancreas
2.2.6.6. Adrenal Gland
2.2.7. Skin and Eye Changes
2.2.7.1. Vascular Changes
2.2.7.2. Pigmentation Changes
2.2.7.3. Tegumentary System
2.2.7.4. Eye Changes
2.2.8. Gastrointestinal Changes
2.2.8.1. Mouth
2.2.8.2. Esophagus and Stomach
2.2.8.3. Intestines
2.2.8.4. Liver
2.2.8.5. Gallbladder
2.2.9. Musculoskeletal Changes
2.2.9.1. Change of Gravity Center
2.2.9.2. Pelvis
2.2.9.3. Musculoskeletal Alterations
2.3. Diagnosis of Pregnancy for Midwives
2.3.1. Pregnancy Diagnosis
2.3.2. Biochemical Tests
2.3.2.1. Biological Tests
2.3.2.2. Immunological Tests
2.3.3. Ultrasound
2.3.4. Signs and Symptoms
2.3.4.1. Signs
2.3.4.2. Symptoms
2.4. Prenatal Care. Midwife’s Program of Gestational Control
2.4.1. Prenatal Care
2.4.2. Pregnancy Control Program
2.4.2.1. First Pregnancy Check-up Visit (< 10 weeks)
2.4.2.2. Subsequent Prenatal Visits
2.4.3. Prenatal Risk Assessment
2.4.4. Prenatal Control Protocols
2.4.4.1. Definition
2.4.4.2. Objectives
2.4.4.3. Involved Personnel
2.4.4.4. Process
2.5. Prenatal Diagnosis
2.5.1. Non-Invasive Techniques
2.5.2. Invasive Techniques
2.5.3. Couple Counseling in Prenatal Diagnosis
2.5.3.1. Definition
2.5.3.2. General Objectives
2.5.3.3. Specific Objectives
2.5.3.4. Target Population
2.5.3.5. Process Description
2.6. Midwife’s Health Education for the Pregnant Woman
2.6.1. Health Education for the Pregnant Woman
2.6.2. Healthy Habits
2.6.2.1. Nutrition
2.6.2.2. Consumption of Harmful Substances
2.6.2.3. Work
2.6.2.4. Exercise
2.6.2.5. Travel
2.6.2.6. Hygiene, Clothing, and Footwear
2.6.2.7. Violence During Pregnancy
2.6.3. Sexuality
2.6.4. Common Discomforts During Pregnancy
2.6.4.1. Cardiovascular
2.6.4.2. Dermatological
2.6.4.3. Digestive
2.6.4.4. Locomotor
2.6.4.5. Respiratory
2.6.4.6. Genitourinary
2.6.5. Warning Signs
2.6.6. Promotion of Breastfeeding
2.6.7. Birth Plan
2.7. Nutrition of the Pregnant Woman
2.7.1. Assessment of the Diet
2.7.1.1. Energy Requirements
2.7.1.2. Food Selection
2.7.1.3. Supplements During Pregnancy
2.7.1.4. Weight Gain
2.7.2. Special Situations
2.7.2.1. Pharmacological Treatment
2.7.2.2. Vegetarian Diet
2.7.3. Dietary Counseling During Pregnancy
2.8. Medications During Pregnancy
2.8.1. Pharmacology During Pregnancy
2.8.2. Mechanisms of Action in the Mother and Fetus
2.8.2.1. Mother
2.8.2.2. Placenta
2.8.2.3. Fetus
2.8.3. Use and Management of Medications During Pregnancy
2.8.4. Indications, Drug Interactions, and Dosage
2.8.4.1. Anti-inflammatories, Analgesics, and Antipyretics
2.8.4.2. Prophylactic Agents for Gastroesophageal Reflux and Antiulcer Drugs
2.8.4.3. Anticoagulants
2.8.4.4. Laxatives
2.8.4.5. Vitamins
2.8.4.6. Antianemics
2.8.4.7. Antiarrhythmics
2.8.4.8. Antihypertensives
2.8.4.9. Hormones
2.8.4.10. Oral Contraceptives
2.8.4.11. Oral Antidiabetics
2.8.4.12. Corticoids
2.8.4.13. Dermatological Treatments
2.8.4.14. Antiviral Treatments
2.8.4.15. Trichomonicides
2.8.4.16. Antibiotics
2.8.4.17. Anti-Asthmatic Medications
2.8.4.18. Antitussives
2.8.4.19. Rhinological Medications
2.8.4.20. Antihistamines
2.8.4.21. Antiepileptics
2.8.4.22. Antidepressants
2.8.4.23. Antipsychotics
2.8.5. Annex. FDA Classification of Different Drug Groups
2.9. Psychosocial Aspects of Pregnancy
2.9.1. Cultural and Religious influences
2.9.2. The Meaning and Impact of Pregnancy on the Couple and on the Family and Social Surroundings
2.9.3. Psychological Changes During Pregnancy
2.9.3.1. First Trimester
2.9.3.2. Second Trimester
2.9.3.3. Third Trimester
2.9.4. Emotional Bonding
Module 3. Maternity Education Program
3.1. History
3.2. Objectives
3.2.1. General Objective
3.2.2. Specific Objectives
3.3. Theoretical and Practical Content
3.3.1. Course Content
3.3.2. Methodology
3.4. Physical Exercises, Pelvic Floor Exercises and Body Statics
3.5. Breathing Techniques
3.5.1. Breathing Classification
3.5.2. Current Trends
3.6. Relaxation Exercises
3.6.1. Theoretical Basis of Childbirth Education
3.6.2. Different Schools
3.7. Use of the Birthing Ball or Spherodynamics
3.8. Aquatic Maternal Education
3.9. Pilates Method for Pregnant Women
Module 4. Labor
4.1. Physiology of Uterine Contraction. Uterine Activity
4.1.1. Basic Physiological Aspects of Uterine Contraction
4.1.2. Basic Biochemistry of Uterine Contraction
4.1.3. Uterine Activity. Brief Historical Review
4.1.4. Components of Uterine Activity
4.1.5. Abdominal Muscles
4.1.6. Causes of Onset of Labor
4.2. Factors Involved in Labor
4.2.1. The Fetus. Fetal Head
4.2.2. Fetal Statics
4.2.3. Leopold’s Maneuvers
4.2.4. Obstetric Nomenclature Determined by Fetal Statics
4.2.5. Diagnosis by Vaginal Examination
4.2.6. Birth Canal
4.2.7. Pelvic Axis
4.2.8. Hodge Planes
4.2.9. Soft Birth Canal
4.2.1. Motor of Labor
4.3. Assessment of Fetal Well-being
4.3.1. Evaluation of Fetal Activity
4.3.2. Non-stress Test (NST)
4.3.3. Stress Test or Contraction Tolerance Test
4.3.4. Biophysical Profile
4.3.5. Amnioscopy
4.3.6. Ultrasound. Doppler Study
4.3.7. Bioelectronic Monitoring in Labor
4.3.8. Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring
4.3.9. Fetal Heart Rate Parameters
4.3.10. Biochemical Monitoring
4.4. Onset of Labor and Periods of Labor
4.4.1. Onset of Labor. Prodromes of Labor
4.4.2. Dilatation Period
4.4.3. Birthing Period
4.4.4. Delivery Period
4.5. Delivery Mechanism in Vertex Presentation
4.5.1. Engagement and Descent in the Upper Pelvic Inlet
4.5.2. Descent and Intrapelvic Rotation
4.5.3. Flexion
4.5.4. Detachment
4.5.5. External Rotation and Shoulder Delivery
4.6. Pharmacology in Labor
4.6.1. Pharmacokinetic Principles
4.6.2. Mechanisms of Action Between the Mother and Fetus
4.6.3. Use and Management of Medications in Labor
Module 5. Assistance and Care for Women During Childbirth
5.1. Assessment and Care of Women
5.1.1. Labor Diagnosis
5.1.2. The Partogram
5.1.3. Assistance and Care of the Woman During Dilatation
5.1.4. Assessment of the Evolution of Labor
5.1.5. Assistance and Care of the Woman During Expulsion
5.1.6. Episiotomy and Episiorrhaphy
5.1.7. Assistance and Care of the Woman during Childbirth
5.1.8. Collection and Donation of Umbilical Cord Blood (UCB)
5.1.9. Birth Assistance Protocol
5.2. Pain Relief During Childbirth. Physiology of Pain During Childbirth. Pain Perception
5.2.1. Physiology of Pain During Childbirth
5.2.2. Characteristics of Pain During Childbirth
5.2.3. Gate Control Theory
5.2.4. Pain Perception During Childbirth
5.2.5. Non-pharmacological Pain Relief Techniques in Labor
5.3. Care During Normal Labor. Birth Plan
5.3.1. Birth Plan
5.3.2. Biomechanics of Labor
5.3.3. Positions that Promote Labor Progression
5.3.4. Protocol for Normal Labor Assistance
5.4. Obstetric Analgesia and Anesthesia
5.4.1. Nitrous Oxide
5.4.2. Opioids
5.4.3. Local Anesthetics
5.4.4. Pudendal Block Anesthesia
5.4.5. Epidural Analgesia
5.4.6. General Anesthesia
5.4.7. Comparative Analysis of Anesthesia Techniques in Cesarean Section
5.5. Assistance for the Woman in Directed Labor
5.5.1. Indications for Induction
5.5.2. Elective Induction
5.5.3. Contraindications for Induction
5.5.4. Risks of Induction
5.5.5. Recommendations for Induction Information. Decision Making
5.5.6. Induction Methods
5.5.7. Labor Stimulation
5.5.8. Assistance and Care of the Woman
5.5.9. Information
5.5.10. Techniques and Movement Restriction
5.5.11. Monitoring of Analgesia
5.5.12. Hydration and Intake
5.5.13. Expulsion Positions
5.6. Psychological Aspects of the Mother During Childbirth
5.6.1. Family Relationship. Family and Professional Support During Childbirth
5.6.2. Psychological Factors During Labor
5.6.3. Psychological Factors During Expulsion
5.6.4. Mother-Child Interactions
5.6.5. Data on Early Skin-to-Skin Contact
5.7. Different Alternatives in Obstetric Care
5.7.1. Hospital Birth
5.7.2. Birthing Centers
5.7.3. Home Birth
5.7.4. Maternal and Perinatal Risk Assessment
Module 6. Nursing Care in the Postpartum Period
6.1. Assistance of the Midwife and Care of the Woman During Postpartum Period
6.1.1. Puerperium, Adaptations, and Modifications
6.1.2. Puerperal Assistance and Care
6.1.3. General Examination
6.1.4. Identification of Problems and Their Prevention
6.1.5. Discharge Counseling
6.2. Psychosocial Aspects in the Puerperium
6.2.1. Psychosocial Adaptation of the Postpartum Woman
6.2.2. Psychological Changes
6.2.3. Emotional Status Assessment: Postpartum Depression Detection
6.2.4. Mother/Partner/Newborn Relationship Bonding
6.2.5. Family Adaptation
6.3. Medications in the Puerperium
6.3.1. Medications in the Puerperium
6.3.2. Use and Management of Medications in the Puerperium. Indications, Drug Interactions, and Dosage
6.4. Home Care by the Midwife During the Puerperium
6.4.1. Characteristics of Home Care of the Mother and the Newborn During the Puerperium
6.4.2. Home Care for the Mother and Newborn in the Puerperium
6.5. Postpartum Care
6.5.1. Postpartum Program
6.5.2. Counseling and Health Education for the Mother-Child Pair
6.5.3. Maternal Recovery. Postpartum Groups
6.5.4. Physical Exercises During the Postpartum Period
6.5.5. Pelvic Floor Recovery
Module 7. Breastfeeding
7.1. Physiology
7.1.1. Milk Secretion
7.1.2. Physiology of Milk Secretion
7.1.3. Inhibition of Milk Secretion
7.2. Breastfeeding
7.2.1. Definition of Breastfeeding
7.2.2. Breastfeeding Practices
7.2.3. Breastfeeding Positions
7.2.4. Manual Expression of Breast Milk
7.2.5. Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative
7.2.6. Advantages of Breastfeeding
7.2.7. Breastfeeding Problems. Special Situations. Breastfeeding in Neonates with Health Problems
7.2.8. Breastfeeding Support Groups (GALM)
7.3. Pharmaceuticals in Lactation
7.3.1. Mechanisms of Action in the Mother and Fetus
7.3.2. Use and Management of Pharmaceuticals in Lactation. Indications, Drug Interactions, and Dosage
Module 8. Nursing Care for the Newborn
8.1. Adaptation to Extrauterine Life
8.1.1. Definition of Newborn or Neonate
8.1.2. Anatomophysiological Recollection of the Fetal Stage
8.1.3. Changes after Birth
8.2. Assessment of the Neonate’s Health Status
8.2.1. Assessment of the Newborn’s Health Status with the Apgar Test
8.2.2. Assessment of Physical Characteristics
8.2.3. Physical Examination of the Newborn
8.2.4. Evaluation of Weight and Gestational Age
8.2.5. Classification of Newborns According to Weight and Gestational Age
8.3. Immediate Care of the Newborn
8.3.1. Introduction
8.3.2. Immediate Care of the Newborn
8.3.3. Immediate Care of the Newborn
8.3.4. Neonatal Resuscitation: Levels
8.4. Anatomical and Physiological Characteristics of the Newborn
8.4.1. Thermal Regulation
8.4.2. Respiratory System
8.4.3. Circulatory System
8.4.4. Digestive System
8.4.5. Urinary System
8.4.6. Hormonal and Immune Changes
8.4.7. Assessment of Neurological Status
8.5. General Care of the Newborn
8.5.1. Care of the Newborn. General Care
8.5.2. Hygiene, Temperature and Umbilical Cord Care
8.5.3. Importance of Aseptic Measures in the Newborn
8.5.4. History of the Newborn
8.5.5. Physical Examination Vital Signs Control
8.5.6. Somatometric Techniques
8.5.7. Mother-Child Interaction and Mother-Partner Relationship Bonding
8.6. Newborn Feeding
8.6.1. Nutritional Needs of the Neonate
8.6.2. Types of Lactation
8.6.3. Artificial Breastfeeding. Concept Formula Feeding
8.6.4. Techniques of Artificial Lactation
8.7. Discharge Counseling
8.7.1. Discharge Counseling. Importance of Parental Counseling at Newborn Discharge
8.7.2. Screening Tests
8.7.3. Signs of Health/ Disease
8.7.4. Immunizations: Schedule
8.7.5. Prevention of Neonatal Accidents
8.7.6. Follow-up Program of the Healthy Child
An online program designed to provide you with the most comprehensive knowledge about the nutritional needs of the newborn”
Master's Degree in Obstetric Nursing
Obstetric Nursing is a fundamental specialty within healthcare, dedicated to providing specialized care to pregnant women and newborns. The complexity and sensitivity of this field require professionals to undergo thorough and rigorous training. With this in mind, TECH Global University has developed the Master’s Degree in Obstetric Nursing—a comprehensive qualification program, optimized through the benefits of digital learning and cutting-edge pedagogical models. Throughout this program, delivered entirely online and with complete flexibility in terms of time and location, you will receive in-depth training in obstetric nursing. Our curriculum, designed by leading specialists, allows you to explore in detail the different stages of pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. In addition, you will acquire specific skills to prevent, detect, and manage potential complications that may arise during these stages.
Expand your knowledge in obstetric nursing
The prestigious business magazine Forbes has recognized us as the best digital university in the world—both for our growth and expansion in a highly competitive market and for the outstanding quality of the more than ten thousand programs we offer in multiple countries. By enrolling in this program, you can be confident that you are choosing the best ally to advance your competencies in obstetric nursing. Our program will provide you with solid theoretical and practical training, enabling you to apply the knowledge acquired directly in your professional practice and truly make a difference in the lives of your patients. Furthermore, you will be supported by a faculty of highly qualified and specialized instructors, who will guide you throughout your learning journey. Thanks to this, you will enhance your professional profile and achieve specialization in the use of innovative technologies and procedures in obstetric care, including electronic fetal monitoring and vertical childbirth.








