University certificate
The world's largest faculty of dentistry”
Why study at TECH?
Improve your knowledge with this program where you will find top level clinical cases and materials. Improve the quality of your clinical practice through this Postgraduate diploma in Clinical Orthodontics”
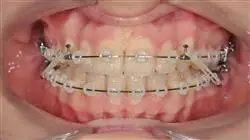
Orthodontics was the first specialty within dentistry and the second after ophthalmology within the health sciences. In this sense, specialty is understood as the possession of a specific professional organization, literature and training. Its peculiarities in diagnosis, type of treatment, objectives and scientific bases, demand an exclusive professional practice.
The knowledge acquired in this program will allow the student to face working life from a more qualified position, giving them a clear advantage when it comes to finding a job, since they will be able to offer the application of the latest technological and scientific advances in the field of periodontics.
The fundamental justification of the program is, therefore, to train professionals with adequate knowledge, skills, attitudes, values and competencies, who is able to serve society by satisfying its health demands, in terms of prevention, diagnosis and treatment, in an ethical, efficient and safe manner.
This professional must appreciate the need for lifelong professional development and continuing education, be able to efficiently utilize advances in knowledge and technology, and understand the central role of the patient in therapeutic decision making.
Expand your knowledge through the Postgraduate diploma in Clinical Orthodontics, in a practical way and adapted to your needs”
This Postgraduate diploma in Clinical Orthodontics includes the most complete and up to date scientific program on the market. The most important features include:
- Clinical cases presented by experts in the different dental specialties
- The graphic, schematic, and practical contents with which they are created provide scientific and practical information on the disciplines that are essential for professional practice
- Latest information on Clinical Orthodontics
- An algorithm-based interactive learning system for decision-making in the clinical situations presented throughout the course
- With a special emphasis on evidence-based medicine and research methodologies in Clinical Orthodontics
- Content that is accessible from any fixed or portable device with an Internet connection
This Postgraduate diploma is the best investment you can make when selecting an up to date program for two reasons: in addition to updating your knowledge in Clinical Orthodontics, you will obtain a Postgraduate diploma from TECH Global University"
Forming part of the teaching staff is a group of professionals in the world of Dentistry, who bring to this course their work experience, as well as a group of renowned specialists, recognised by esteemed scientific communities.
The multimedia content developed with the latest educational technology will provide the professional with situated and contextual learning, i.e., a simulated environment that will provide immersive training program to train in real situations.
This program is designed around Problem Based Learning, whereby the professional must try to solve the different professional practice situations that arise throughout the program. For this reason, you will be assisted by an innovative, interactive video system created by renowned and experienced experts in the field of radiology with extensive teaching experience.
This Postgraduate diploma offers training in simulated environments, which provides an immersive learning experience designed to train for real life situations"
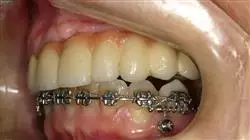
It includes clinical cases to bring the program's degree as close as possible to the reality of care in dentistry"
Syllabus
The structure of the content has been designed by a team of professionals who recognize the implications of specialization in daily dentistry practice, who are aware of the relevance of current training to treat patients, and who are committed to quality teaching using new educational technologies.
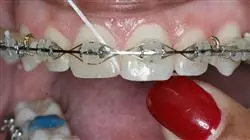
This Postgraduate diploma in Clinical Orthodontics includes the most complete and up to date scientific program on the market”
Module 1. Initial Diagnosis
1.1. Systematic Diagnosis in Dentistry
1.1.1. First Visit and Clinical History
1.1.2. Patient Exploration
1.1.3. Ordinary Records
1.1.4. Complementary Records
1.1.5. Myofunctional Records
1.2. Staged Orthodontic Diagnosis
1.2.1. Establishing Problem Listing
1.2.2. Establishing Therapeutic Objectives
1.2.3. Mechanotherapy Planning and Equipment
Module 2. Advanced Diagnosis
2.1. Cephalometric Analysis 3D Diagnosis CBCT y CT
2.1.1. Cephalometric Analysis
2.1.1.1. Introduction
2.1.1.2. Craniometric Points Description
2.1.1.3. Steiner Cephalometric Analysis
2.1.1.4. Ricketts Cephalometric Analysis
2.1.2. 3D Diagnosis
2.1.2.1. Introduction
2.1.2.2. System Fundamentals
2.1.2.3. CBCT vs. Computerized Tomography
2.1.2.4. Advantages
2.1.2.5. Disadvantages
2.1.2.6. Voxel
2.1.2.7. Image Interpretation
2.1.2.8. Radiation
2.1.2.9. Clinical Application of CBCT
2.2. Diagnosis and Treatment of Habits
2.2.1. Introduction
2.2.2. Atypical Swallowing in Children
2.2.3. Nutritional Sucking Habits
2.2.3.1. Breastfeeding
2.2.3.2. Feeding Bottles
2.2.4. Non-Nutritional Sucking Habits
2.2.4.1. Digital Sucking
2.2.4.2. Pacifier Habits
2.2.5. Mouth Breathing
2.2.6. Dyslalia
2.2.7. Other Habits
2.3. Early Diagnosis of Patients at Risk
2.3.1. Caries and White Spots: Current Techniques Preventive Treatment for Enamel Demineralization
2.3.2. Root Resorptions. Current Techniques. Preventive Treatment for Root Resorption
2.3.3. Differential Diagnosis of the Most Frequent Temporomandibular Disorders in Orthodontic Patients
2.3.4. Idiopathic Condylar Resorption: Current Diagnostic Techniques. Preventive Treatment for Severe Progressive Open Bite
Module 3. Malocclusions and Dentofacial Deformities Etiology
3.1. Craniofacial Growth and Development
3.1.1. Types of Postnatal Growth
3.1.2. Integrating Facial Development
3.1.3. Upper Jaw Growth
3.1.4. Jaw Growth
3.2. Tooth Eruption Pathophysiology
3.2.1. Eruption Phases
3.2.2. Tooth Eruption in Adults
3.2.3. Eruption Mechanisms
3.2.4. Dentition General Development
3.3. Dentoalveolar Growth and Adaptation in Different Malocclusions and Dentofacial Deformities
3.3.1. Dentoalveolar Growth and Adaptation in Transverse Malocclusions
3.3.2. Dentoalveolar Growth and Adaptation in Vertical Malocclusions
3.3.3. Dentoalveolar Growth and Adaptation in Sagittal Malocclusions
3.4. Differential Diagnosis of Etiological Factors
3.4.1. Malocclusion Etiological Factors
3.4.2. Specific Causes of Malocclusion
3.4.3. Genetic Influences
3.4.4. Environmental Influences
3.4.5. Current Etiological Perspective
Module 4. Treatment Plan
4.1. Concepts and Objectives
4.1.1. Establishing Priority Lists for Orthodontic Problems
4.1.2. Establishing Treatment Possibilities and Therapeutic Sequencing
4.1.3. Assessing Potential Treatment Factors
4.1.4. Types of Treatment
4.1.5. Treating Orthodontic Disorders
4.2. Evidence-Based Orthodontics: PICO, Databases and Critical Reading
4.2.1. Formulating Clinical Questions
4.2.2. Literature Consultation
4.2.3. Types of Clinical Studies
4.2.4. Bias and Confusion Factors
4.2.5. Evidence Levels and Degrees of Recommendation
4.2.6. Critical Assessment of Results
4.3. Limits to Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics as a Function of Malocclusion Type and Patient Age
4.3.1. Growth Modification in Skeletal Problem Treatments
4.3.2. Biological Limits
4.3.3. Soft Tissue Limitations
4.4. Early or Late Treatment Indications
4.4.1. Determining Skeletal Maturity
4.4.2. Malocclusion Evolution during Growth
4.4.3. Early Treatment for Malocclusions
4.5. Determining the Need for Therapeutic Extractions
4.5.1. Definition of Volumetric Malocclusions
4.5.2. Premolar Therapeutic Extractions
4.5.3. Special Extraction Cases
4.5.4. Stripping Technique as an Alternative to Tooth Extractions
4.6. Preparing Individualized Treatment Plans
4.6.1. General Considerations in Individualized Treatment Planning
4.6.2. Determining Individualized Treatment Plans
4.6.3. Auxiliary Tools to Determine Individual Treatment Plans: The Steiner Box
Module 5. Conventional Orthodontics
5.1. Treatments for Stage 2 Mixed and Early Permanent Dentition
5.1.1. Treatment Protocols
5.1.2. Indications and Contraindications. Fixed Equipment
5.1.2.1. Advantages and Disadvantages. Fixed Equipment
5.1.3. Malocclusions
5.1.3.1. Transversal Malocclusions
5.1.3.2. Vertical Malocclusions
5.1.4. Retention/Relapse
5.2. Bracket Cementation Specification: Malocclusion Type and/or Therapeutic Objectives
5.2.1. Installing Pre-Adjusted Equipment
5.2.1.1. Bracket and Tube Location
5.2.1.2. Mesiodistal Location
5.2.1.3. Vertical Position (“Height”)
5.2.1.4. Inclination
5.2.1.5. Vestibular Face Fitting
5.2.2. Cementing in Case of Deep Spee Curve
5.2.3. Cementing in Case of Class II Molar
5.2.4. Cementing in Fractured or Abraded Teeth
5.3. First Phase: Alignment and Leveling Types of Intrusion
5.3.1. Diet
5.3.1.1. Selection Principles for Alignment Arches
5.3.1.2. Symmetric Crowding Alignment
5.3.1.3. Alignment in Case of Premolar Extraction
5.3.1.4. Alignment in Non-Extraction Cases
5.3.2. Levels
5.3.2.1. Extrusion Leveling (Relative Intrusion)
5.3.2.2. Intrusion Leveling
5.4. Second Phase: Work, Closing Extraction Spaces
5.4.1. Molar Ratio Correction
5.4.1.1. Differential Growth in Class II Patients
5.4.1.2. Differential Anchoring of Extraction Spaces
5.4.1.3. Distalization
5.4.2. Closing Extraction or Residual Spaces
5.4.2.1. Continuous Bow with Locking Handles or DKL Bow
5.4.2.2. Sliding
5.4.3. Overjet and Overbite Correction
5.4.4. Middle Line Centering
5.5. Third Phase: Completion Retention Design
5.5.1. Retention Definition
5.5.2. Types of Retainers
5.5.2.1. Fixed Retainers
5.5.2.2. Removable Retainers
5.5.3. Retention Duration
5.5.3.1. Cases Where Retention May Not Be Required
5.5.3.2. Cases Requiring Permanent or Semipermanent Retention
5.5.3.3. Cases Requiring a Variable Retention Period
Module 6. Multidisciplinary Treatments
6.1. Treating Periodontal Patients
6.1.1. Specific Characteristics in Adult Patients
6.1.2. Anatomy of the Periodontium
6.1.3. Multidisciplinary or Interdisciplinary Treatments
6.1.4. Diagnosing Adult Patients and Determining Treatment Goals
6.1.5. Preparing Adult Orthodontic Patients for Orthodontic Treatment
6.1.6. Stripping Tool as an Essential Element in Adult Periodontal Patients
6.1.7. A Special Entity: Posterior Bite Collapse in Adult Patients
6.2. Treatment and Esthetics in Anterior Fronts: Orthodontics and Prosthetics
6.2.1. Fundamental Requirements for Successful Occlusal Therapy as Proposed by Dawson
6.2.2. The Six Decisions Affecting the Functional Anatomy Matrix
6.2.3. Previous Guidelines
6.2.4. Fundamental Esthetic Criteria
6.3. Orthodontics and Treating SAHS in Children
6.3.1. Anatomy of the Respiratory System
6.3.2. Lymphoid System
6.3.3. General Sleep Concepts: Sleep and Breathing
6.3.4. Clinical Examination in Children with Suspected SAHS
6.4. Orthodontics and Treating SAHS in Adults
6.4.1. Sleep Medicine
6.4.2. Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome (SAHS)
6.4.3. Efficacy of Mandibular Advancement Devices (MADs)
6.4.4. Therapy Management and Monitoring Protocol
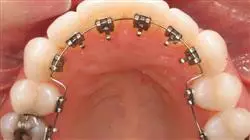
A unique, key and decisive training experience to boost your professional development”
Postgraduate Diploma in Clinical Orthodontics
In the medical sciences, in the specialized world of dentistry, it is expected that the health of patients will be protected by initially managing a diagnosis that takes into account all types of of factors that affect the correct positioning of the teeth; since, it can cause various physical, aesthetic and functional problems that can also negatively impact multiple organs of the digestive system and some muscles that surround the mouth and head. Thus, it is important that professionals have the necessary knowledge in this area to be able to take precedence, act and maintain periodic controls in each particular case. For this reason, a Postgraduate Diploma in Clinical Orthodontics was created at TECH Global University in which it will be possible to understand the latest techniques in the field of dental care and thus stand out in the private or public labor sector and improve the quality of life of patients.
Deepen your knowledge to be a Clinical Orthodontist online
This curriculum is developed over six months and is made up of six modules, which will address initial and advanced diagnosis, etymology of malocclusions and dentofacial deformities, treatment plan, conventional orthodontics and multidisciplinary treatments. All this was designed with the objective of providing an understanding of the main and most developed, theoretical and practical concepts that will help control the techniques necessary for professional practice. In the academic program, each of the themes created will be studied in depth, where the conceptual will be worked on from an integral structure, having completely digital fundamental tools that will help guide the learning process and accompanied by updated literature, so that the student establishes himself. on a paradigm and continue with a specific planning and act depending on each particular case.







