University certificate
The world's largest faculty of nursing”
Why study at TECH?
Knowing the peculiarities of the emergency department will be fundamental for your professional development in this area, but, above all, for adult and pediatric patient specialized care”
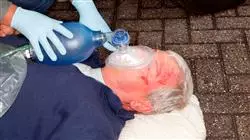
Healthcare in emergency situations is more complex than in other areas, since, given each patient's situation, the first intervention and diagnosis may be complicated. The sick or injured person in need of urgent or emergency care presents acute symptoms, in various forms, which change and evolve in a short period of time. They could be fighting for their lives, depending on which organs are affected, and they may need rapid response care to be saved.
Moreover, the organization of services for patient care in urgent and emergency situations often differentiates between adults and children, which explains why students can find different programs to specialize in emergency nursing. However, this has also created a need for those professionals who are looking for comprehensive, useful and relevant specialization to be able to intervene in all types of patients.
To this end, this program compiles the best of emergency nursing studies, urgent response and catastrophes, as well as the most relevant aspects of pediatric emergencies for nurses, so that they acquire a global and specialized knowledge of the factors that can affect all patients. Specifically, it presents the means and equipment available for urgent interventions, their applications and complications so that they can be used appropriately in each emergency situation, including basic and advanced life support, which is essential for critical patients. Furthermore, taking into account the current COVID-19 pandemic, the program includes a specific syllabus to explain its microbiological characteristics, diagnostic tests and treatments, as well as ways of intervening in coronavirus patients.
It should be noted that this program is totally different from others that can be found on the market, since it places experience as the foundation of the theory, providing global and sufficient knowledge to practice.
When pediatric patients get to the emergency room, they require specialized care that you will learn about by studying this Advanced Master's Degree”
This Advanced master’s degree in Emergency Nursing in Adult and Pediatric Patients is the most complete and up-to-date program on the market. The most important features include:
- Practical cases presented by experts in Emergency Nursing
- The graphic, schematic, and eminently practical contents with which they are created, provide scientific and practical information on the disciplines that are essential for professional practice
- Practical exercises where self-assessment can be used to improve learning
- Special emphasis on innovative methodologies in Emergency Nursing
- Theoretical lessons, questions to the expert, debate forums on controversial topics, and individual reflection assignments
- Content that is accessible from any fixed or portable device with an Internet connection
TECH is a 21st century university and is committed to online teaching as its main method of learning”
The teaching staff includes nursing professionals who bring their experience to this training program, as well as renowned specialists from leading societies and prestigious universities.
The multimedia content, developed using the latest educational technology, will provide the professional with situated and contextual learning, i.e., a simulated environment that will provide an immersive training experience designed to train for real-life situations.
This program is designed around Problem-Based Learning, whereby the student must try to solve the different professional practice situations that arise during the course. For this purpose, the professional will be assisted by an innovative interactive video system created by renowned and experienced experts.
Specialize in emergency nursing and learn to care for adult and pediatric patients with different conditions"
A 100% online update that will allow you to balance your studies with the rest of your daily obligations"
Syllabus

A complete syllabus that will guide you through the main techniques and procedures used in nursing emergencies”
Module 1. General aspects
1.1. Definitions and Concepts
1.2. Comprehensive Study of Health Emergencies
1.3. Functions of Emergency and Disaster Nursing
1.4. Bioethics in Emergencies and Disasters
Module 2. Hospital Emergency Services
2.1. Organization of Hospital Emergency Services
2.2. Nursing Records in the Emergency Department
2.3. Triaje Systems in Hospitals
Module 3. Emergency Services and Healthcare Transport
3.1. SEM Organization
3.2. Coordination and Health Regulation
3.3. Information and Record Systems
3.4. Types of Medical Transport
3.4.1. Intrahospital Transport
3.4.2. Interhospital Transport
3.4.3. Ground Medical Transport
3.4.4. Air Medical Transport
3.5. Types of Out-of-Hospital Health Resources
3.6. Pathophysiology of Medical Transport and Transfer Positions
3.7. Patient Transfer Models
3.8. Transport and Emergencies Legislation
Module 4. Life Support
4.1. General aspects
4.2. Basic Life Support and AED in Adults
4.3. Basic Life Support and AED in Children
4.4. Basic Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias
4.5. Advanced Life Support in Adults
4.6. Advanced Pediatric Life Support
4.7. Neonatal Resuscitation
4.8. Resuscitation in Special Cases
Module 5. Medical-Surgical Emergencies in Adults (I)
5.1. Cardiovascular Emergencies
5.1.1. Ischemic Heart Disease
5.1.2. Cardiac Contractility Disorders: CHF, PAD, Cardiogenic Shock, Cardiac Tamponade
5.1.3. Vascular Emergencies
5.1.4. Inflammatory-Infectious Disorders: Pericarditis, Myocarditis, Endocarditis
5.1.5. Aortic Dissection and Aneurism
5.1.6. Deep Vein Thrombosis
5.1.7. Pulmonary Embolism
5.1.8. Pulmonary Hypertension
5.1.9. Acute Peripheral Vascular Disease
5.1.10. Hypertensive Crisis
5.2. Respiratory Emergencies
5.2.1. Anatomophysiological Review of the Respiratory System
5.2.2. Acute Respiratory Failure
5.2.3. ARDS
5.2.4. Asthma and Asthmatic Status
5.2.5. Bronchitis, Bronchiolitis, Pneumonia
5.2.6. Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
5.2.7. Pleuritis and Pleural Effusion
5.3. Neurological Emergencies
5.3.1. Anatomophysiological Review of the Nervous System
5.3.2. Neurological Evaluation for Critically Ill Patients Most Common Scales
5.3.3. Vascular Disorders: Stroke, Transient Ischemic Attack, Subarachnoid Hemorrhage, Subdural and Extradural Hematoma, Venous Thrombosis of the Sinuses
5.3.4. Inflammatory-Infectious Disorders: Meningitis, Encephalitis, Meningococcal Sepsis, Peripheral Facial Paralysis, Trigeminal Neuralgia
5.3.5. Syncope, Coma, Headache, Acute Confusional Syndrome, Dizziness, Vertigo
5.3.6. Vertigo
5.3.7. Seizures and Status Epilepticus
5.3.8. Intracranial Hypertension
5.4. Digestive Emergencies
5.4.1. Anatomophysiological Review of the Digestive System
5.4.2. Acute Abdomen and Abdominal Pain
5.4.3. Vascular Disorders: Esophageal Varices, Ischemic Colitis, Hemorrhage, Mesenteric Ischemia
5.4.4. Inflammatory-Infectious Disorders: Reflux Esophagitis Caustic Injuries Appendicitis, Cholecystitis, Cholangitis, Diverticulitis, Exacerbations and Complications of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Gastritis, Gastroenteritis, Peptic Ulcer, Hepatitis, Pancreatitis, Peritonitis Acute Complications of Cirrhosis Fulminant Liver Failure and Hepatorenal Syndrome
5.4.5. Trauma and Mechanical Problems: Foreign Bodies, Esophageal Rupture and Tear, Hernia Strangulation, Intestinal Obstruction and Occlusion Gastric Volvulus
5.4.6. Acute Anal Disease
Module 6. Medical-Surgical Emergencies in Adults (II)
6.1. Nephrourological Emergencies
6.1.1. Anatomophysiological Review of the Genitourinary System
6.1.2. Renal and Excretory System Lithiasis
6.1.3. Urinary Retention
6.1.4. Inflammatory/ Infectious Disorders
6.1.5. Acute Renal Failure
6.1.6. Hematuria
6.1.7. Acute Scrotal Syndrome: Testicular Torsion
6.1.8. Acute Urethral Disease
6.2. Endocrinometabolic and Hydroelectrolytic Emergencies
6.2.1. Thyroid Diseases
6.2.2. Acid-base Balance Disorders
6.3. Hematological, Immunological and Infectious Emergencies
6.3.1. Allergies and Anaphylactic Reactions
6.3.2. Sepsis and Septic Shock
6.3.3. Febrile Syndrome
6.4. Intoxications
6.4.1. General Aspects of an Intoxicated Patient
6.4.2. Attitude toward the Most Common Intoxications: Alcohol, Sedatives and Hypnotics, Hallucinogens and Designer Drugs, Antidepressants, AAS and Paracetamol, Corrosive Drugs and Others
6.5. Obstetrical-Gynecological Emergencies
6.5.1. Inflammatory-Infectious Disorders: Mastitis, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Vulvovaginitis
6.5.2. Hemorrhages
6.5.3. Pregnancy and Postpartum Emergencies
6.5.4. Emergency Delivery Assistance
6.5.5. Sexual Abuse
6.6. Psychiatric Emergencies
6.6.1. Psychopathology
6.6.2. Psychomotor Agitation
6.6.3. Acute Alcoholic Disease
6.6.4. Self-Harm Attempt
6.6.5. Anxiety Attack
6.6.6. Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Module 7. Other Emergencies
7.1. Pediatric Emergencies
7.1.1. Infantile Colic
7.1.2. Fever Syndrome in Children
7.1.3. Febrile Seizures
7.1.4. Abdominal Pain, Vomiting, Diarrhea
7.1.5. Child Abuse
7.1.6. Transport of Critical Pediatric Patients
7.2. Otolaryngologic Emergencies
7.2.1. Angioedema, Epiglottitis, Laryngitis, Paratonsillar Abscess
7.2.2. Foreign Bodies in ENT
7.2.3. Epistaxis
7.2.4. Angioedema
7.2.5. Acute Hearing Loss
7.3. Ophthalmologic Emergencies
7.3.1. Anatomy Recap of the Eye
7.3.2. Non-painful Red Eye
7.3.3. Painful Red Eye
7.3.4. Extraocular Foreign Body
7.3.5. Intraocular Foreign Bodies
7.4. Skin Emergencies
7.5. Terminal Patient in Emergencies
7.5.1. Emergency Complications in Terminal Patients
7.5.2. Attention to the Situation in the Last Few Days of a Terminal Patient’s Life
7.6. Encephalic Death and Organ and Tissue Donation Process
Module 8. Adult and Pediatric Severe Trauma Care
8.1. General aspects
8.2. Biomechanics of Accidents
8.3. Primary and Secondary Evaluation
8.4. TBI
8.5. Thoracic Trauma
8.6. Abdominal Trauma
8.7. Vertebral Trauma and Spinal Cord Injury
8.8. Trauma of the Locomotor System
8.9. Injuries
8.10. Hypovolemic Shock
8.11. Pediatric Trauma
8.12. Trauma During Pregnancy
8.13. Special Traumas
8.13.1. Crush Syndrome
8.13.2. Shock or Blast Wave Injuries
8.14. Injuries due to Physical, Chemical and Environmental Agents
8.14.1. Bites and Stings
8.14.2. Dysbarism
8.15. Analgesia and Sedation
8.16. Mobilization and Immobilization Materials and Techniques
8.17. Rescue and Medical Care in Confined and Remote Places
Module 9. Multiple Victim Incidents and Disasters
9.1. General Concepts
9.2. IMV Management and Disasters
9.3. Sectorization
9.4. Deployment and Logistics
9.5. Triage
9.6. Multiple Victim Care
9.7. Evacuation
9.8. MCI Management in a Hospital
9.9. CBRN Incidents
9.9.1. Individual Protection Equipment
9.10. Emergency Planning
Module 10. Pharmacology of Accidents and Emergencies
10.1. Basic Concepts
10.2. Drug Administration Routes in Accidents and Emergencies
10.3. Drug Administration Safety
10.4. Fluid Therapy
10.5. Most Common Drugs Used in Accident and Emergency Care
10.6. Formulas and Dose Calculation
Module 11. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Techniques in Accident and Emergency Care
11.1. Probes
11.2. Peripheral and Central Vein Cannulation
11.3. Intraosseous Route
11.4. Orotracheal Intubation (OTI)
11.5. Management of Difficult VA
11.6. Mechanical Ventilation
11.7. Use of Non-invasive Mechanical Ventilation
11.8. Pericardiocentesis
11.9. Thoracentesis
11.10. Ultrasound for Nurses Eco-guided Techniques
11.11. Electrical Therapy (MMP, CV, DF)
11.12. Monitoring of Neurological Status
11.13. Monitoring of Sedoanalgesia
11.14. Collecting Analytical Samples
11.15. Frequently Used Scales in Accident and Emergency Medicine
11.16. Physiological Parameters in Adults and Children
Module 12. Other important Aspects in Caring for a Critically Ill Patient
12.1. Patient Security
12.2. Teamwork. Communication and Leadership
12.3. New Professional Skills in Accident and Emergency Care
12.4. New Technologies in Accident and Emergency Care
Module 13. Health Care Organization for Pediatric Emergencies
13.1. Equipment in the Pediatric Emergency Department (PED)
13.1.1. Differential Characteristics of PEDs
13.1.2. Infrastructure, Staffing
13.1.3. Material
13.2. Triage in Pediatrics
13.2.1. Definition
13.2.2. Classification Systems
13.3. Transport of Critical Pediatric Patients
13.3.1. Intrahospital Transfer
13.3.2. Neonatal and Pediatric Transportation
Module 14. Advanced Pediatric and Neonatal Cardiovascular Support
14.1. Apparently Lethal Syndromes
14.1.1. Muerte súbita del lactante
14.1.2. Treatment
14.1.3. Home Monitoring
14.2. Recognition and Management of Critically Ill Children
14.2.1. Epidemiology, Etiology and Prevention of CRP in Childhood
14.2.2. Pediatric Assessment Triangle (PAT) and its Utility
14.2.3. Pediatric ABCDE Evaluation
14.3. Basic Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
14.4. Advanced Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Advanced Airway Management
14.5. Basic Concepts of Mechanical Ventilation
14.6. Infusion Routes and Drugs
14.7. Pediatric AVS Algorithms and Treatment of Arrhythmias
14.8. Neonatal Resuscitation
14.9. Post-resuscitation Stabilization and Neonatal Transport
Module 15. Invasive Techniques in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients
15.1. Peripheral and Central Vein Access
15.1.1. Peripheral Route
15.1.2. Central Route
15.2. Intraosseous Puncture
15.3. Capnography, Pulse Oximetry
15.4. Oxygen Therapy
15.5. Rapid Intubation Sequence
15.6. Analgesia and Sedation
15.6.1. Approaching Pain
15.6.2. Procedure
15.6.3. Reference Drugs in Analgesia and Sedation
15.7. Protocol for Child Death
Module 16. Pediatric Nursing Care in Cardiology Emergencies
16.1. Arrhythmias and Syncope
16.1.1. Bradyarrhythmias Diagnosis and Treatment
16.1.2. Tachyarrhythmias Diagnosis and Treatment
16.2. Congenital Heart Disease
16.2.1. Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
16.2.2. Non-Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
16.2.3. Diagnostic Approach
16.2.4. Treatment
16.3. Hypertensive Crisis
16.3.1. Diagnostic Guidance for Hypertension in Children and Adolescents
16.3.2. Therapeutic Guidance for Hypertension in Children and Adolescents
16.4. Heart Failure
16.4.1. Etiology
16.4.2. Diagnosis
16.4.3. Treatment Mechanical Ventricular Assistance Techniques Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)
16.5. Techniques and Procedures
16.5.1. Quick Reading of an ECG
16.5.2. Defibrillation
16.5.3. Cardioversion and Temporary Pacemaker
Module 17. Nursing Care in Respiratory Emergencies
17.1. Respiratory Pathology in Recent Newborns
17.1.1. Incomplete Pulmonary Fluid Reabsorption Syndrome
17.1.2. Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
17.1.3. Hyaline Membrane Disease
17.1.4. Pneumothorax
17.1.5. Pneumonia
17.1.6. Apnea in Newborns
17.2. Airway Diseases
17.2.1. Acute Pharyngotonsillitis
17.2.2. Laryngitis or Croup
17.2.3. Spasmodic Croup
17.2.4. Otitis
17.2.5. Sinusitis
17.3. Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
17.3.1. Diagnosis
17.3.2. Hospital Admission Criteria
17.3.3. Latest Advances in Treatment
17.4. Managing a Child with a Persistent Cough. Chronic Cough
17.4.1. Etiology
17.4.1.1. Persistent Bacterial Bronchitis
17.4.1.2. Asthma
17.4.1.3. Gastroesophageal Reflux, etc
17.4.2. Treatment
17.5. Caring for Asthmatic Children
17.5.1. Clinical Diagnosis. Functional Diagnosis
17.5.2. Pharmacological Treatment. Non-Pharmacological Treatment
17.5.3. Education of Health
17.6. Techniques and Procedures
17.6.1. Inhalation Techniques Oxygen Therapy
17.6.2. Thoracentesis and Chest Tube Placement
17.6.3. Forced Spirometry Bronchodynamic Tests PEF (Peak Expiratory Flow Meter Management)
Module 18. Nursing Care for Unintentional Injuries Child Accidents
18.1. Burns and Wounds
18.2. Drowning
18.3. Stings and Bites
18.4. Drug and Non-drug Intoxications
18.5. Anaphylaxis
18.5.1. Classification of Severity
18.5.2. Diagnostic Procedures
18.5.3. Treatment and Discharge Recommendations
18.6. Techniques and Procedures
18.6.1. Extraction of Foreign Body from the Ear
18.6.2. Extraction of Foreign Bodies from the Nose
18.6.3. Incarcerated Inguinal Hernia Reduction
18.6.4. Freeing of Trapped Penis or Scrotum
Module 19. Nursing Care in Pediatric Trauma and Osteoarticular Injuries
19.1. Initial Pediatric Trauma Care
19.1.1. Types and Patterns of Injury in Pediatrics
19.1.2. Primary and Secondary Assessment
19.1.3. Spinal Cord Injuries
19.2. Head Trauma in Children
19.3. Limping
19.3.1. Types of Lameness
19.3.2. Treatment
19.3.3. Referral Criteria
19.4. Upper Extremity Trauma
19.5. Lower Extremity Trauma
19.6. Thoracic Trauma Rib Fractures and Contusions
19.7. Techniques and Procedures
19.7.1. Mobilization and Immobilization Workshop
19.7.2. Painful Pronation Reduction
19.7.3. Hyperpronation
19.7.4. Supination-Flexion
19.7.5. Active Mobilization Stimulation
19.7.6. Classification of Pediatric Fractures
Module 20. Nursing Care in Neurological Emergencies
20.1. Alterations of Consciousness
20.2. Bacterial and Viral Meningitis
20.3. Febrile Seizures
20.4. Acute Headache
20.4.1. Migraine
20.4.2. Tension Headache
20.4.3. Periodic Syndromes of Childhood
20.5. Epilepsies and Non-Epileptic Seizure Disorders in Childhood
20.5.1. Epileptic Syndromes in Childhood and Adolescence
20.5.2. General Treatment of Epilepsies
20.6. Acute Ataxia
20.7. Techniques and Procedures
20.7.1. Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Puncture
20.7.2. Lumbar Puncture
Module 21. Nursing Care in Digestive Emergencies
21.1. Acute Abdominal Pain
21.2. Gastrointestinal Disorders
21.3. Acute Dehydration
21.3.1. Isonatremic Dehydration
21.3.2. Hyponatremic Dehydration
21.3.3. Hypernatremic Dehydration
21.4. Acid-base Balance Disorders
21.4.1. Metabolic Acidosis. Respiratory Acidosis
21.4.2. Metabolic Alkalosis. Respiratory Alkalosis
21.5. Coeliac Disease
21.5.1. Diagnostic Algorithm
21.5.2. Treatment
21.6. Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER)
21.7. Constipation
21.8. Hepatitis
21.8.1. HAV, HBV, HCV, HDV, HEV
21.8.2. Autoimmune hepatitis
21.9. Gastrointestinal Bleeding
21.10. The Infant with Food Refusal
21.11. Jaundice
21.12. Techniques and Procedures
21.12.1. Inguinal Hernia Reduction
21.12.2. Gastric Explorations
21.12.3. Managing Children Suffering from Ostomy
Module 22. Nursing care in Endocrinometabolic Emergencies
22.1. Emergencies in the Diabetic Patient
22.2. Hydroelectrolytic Alterations
22.3. Adrenal Insufficiency
Module 23. Nursing Care in Infectious Emergencies
23.1. Exanthematous Diseases
23.2. Whooping Cough and Pertussis Syndrome
23.2.1. Medical treatment
23.2.2. Control Measures
23.3. Febrile Syndrome without Focus
23.4. Sepsis. Septic Shock
23.5. Osteoarticular Infections
23.6. Fever and Neutropenia
Module 24. Nursing Care in Ophthalmological and Otorhinolaryngology Emergencies
24.1. Conjunctivitis and Blepharitis Pink Eye
24.1.1. Most Frequent Infectious Pathology
24.1.2. Non-Infectious Pathology
24.1.3. Protocol for Pediatric Ophthalmologic Emergencies
24.2. Eyelids and Lacrimal System
24.2.1. Palpebral Alterations and Malformations
24.2.2. Inflammatory Pathology
24.2.3. Cysts and Tumors
24.2.4. Lacrimal Pathology in Children
24.2.5. Palpebral Traumatology in Infancy
24.3. Acute Pharyngotonsillitis Acute Otitis Media Sinusitis
24.4. Techniques and Procedures
24.4.1. Managing Children Suffering from Tracheostomy
24.4.2. Fluorescein and Eversion Inspection
24.4.3. Extraction of Foreign Bodies from the Eye
24.4.4. Ophthalmologic Examination with Fluorescein
24.4.5. Eversion of the Upper Eyelid
Module 25. Nursing Care in Nephrourologic Emergencies
25.1. Urinary Infections
25.1.1. Diagnostic Criteria
25.1.2. Referral Indications
25.2. Hematuria
25.3. Renal Lithiasis and Renal Colic
25.4. Acute Scrotum
25.4.1. Frequency in the Pediatric Age Group
25.5. Techniques and Procedures
25.5.1. Suprapubic Puncture
25.5.2. Bladder Catheterization
25.5.3. Reduction of Paraphimosis
Module 26. Nursing Care in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients
26.1. Communication with the Pediatric Intensive Care Patient
26.2. Most Common Alterations
26.3. Evaluating Critical Pediatric Patients
26.3.1. Needs Assessment
26.3.2. Most Common Pediatric Rating Scales
26.4. Pediatric Assessment Triangle
26.5. Critical Pediatric Patient Care
26.5.1. Airway and Ventilatory Management for Critically Ill Pediatric Patients
26.5.2. Nursing Techniques in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients: Monitoring, Venous Access, Safety and Comfort
26.5.3. Administrating Medication for Pediatric Patients
26.5.4. Interhospital Transport for Critically Ill Pediatric Patients
26.6. Administering Drugs
26.6.1. Peripheral Vein Routes
26.6.2. Intraosseous Route
26.6.3. Intratracheal Route
26.6.4. Central Routes
26.6.5. Most Used Drugs and Fluids
Module 27. Nursing Care in Special Emergency Situations
27.1. Children with Special Needs
27.1.1. Tracheostomy and Home Mechanical Ventilation
27.1.2. Gastrostomies and Feeding Tubes
27.1.3. Peritoneal Ventriculo-Peritoneal Shunt Valves
27.1.4. Central Catheters and Prosthetic Vascular Accesses
27.2. Medication in Pediatrics
27.3. Psychiatry in the Emergency Department
27.3.1. Assessment and Initial Treatment
27.3.2. Psychomotor Agitation and Violence
27.3.3. Suicidal Behavior
27.3.4. Psychotic Disorders
27.4. Child Abuse
27.4.1. Attitude in the Emergency Room
27.4.2. Assistance in the Case of Abuse
27.5. Techniques and Procedures
27.5.1. Mechanical Restraint of the Agitated or Aggressive Child
Module 28. Update on Coronavirus Infections
28.1. Discovery and Evolution of Coronaviruses
28.1.1. Discovery of Coronaviruses
28.1.2. Global Trends in Coronavirus Infections
28.2. Main Microbiological characteristics and Members of the Coronavirus Family
28.2.1. General Microbiological Characteristics of Coronaviruses
28.2.2. Viral Genome
28.2.3. Principal Virulence Factors
28.3. Epidemiological Changes in Coronavirus Infections from its Discovery to the Present
28.3.1. Morbidity and Mortality of Coronavirus Infections from their Emergence to the Present
28.4. The Immune System and Coronavirus Infections
28.4.1. Immunological Mechanisms Involved in the Immune Response to Coronaviruses
28.4.2. Cytokine Storm in Coronavirus Infections and Immunopathology
28.4.3. Modulation of the Immune System in Coronavirus Infections
28.5. Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Coronavirus Infections
28.5.1. Pathophysiological and Pathogenic Alterations in Coronavirus Infections
28.5.2. Clinical Implications of the Main Pathophysiological Alterations
28.6. Risk Groups and Transmission Mechanisms of Coronaviruses
28.6.1. Main Sociodemographic and Epidemiological Characteristics of Risk Groups Affected by Coronavirus
28.6.2. Coronavirus Mechanisms of Transmission
28.7. Natural History of Coronavirus Infections
28.7.1. Stages of Coronavirus Infection
28.8. Latest Information on Microbiological Diagnosis of Coronavirus Infections
28.8.1. Sample Collection and Shipment
28.8.2. PCR and Sequencing
28.8.3. Serology Testing
28.8.4. Virus Isolation
28.9. Current Biosafety Measures in Microbiology Laboratories for Coronavirus Sample Handling
28.9.1. Biosafety Measures for Coronavirus Sample Handling
28.10. Up-to-Date Management of Coronavirus Infections
28.10.1. Prevention Measures
28.10.2. Symptomatic Treatment
28.10.3. Antiviral and Antimicrobial Treatment in Coronavirus Infections
28.10.4. Treatment of Severe Clinical Forms
28.11. Future Challenges in the Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus
28.11.1. Global Challenges for the Development of Prevention, Diagnostic, and Treatment Strategies for Coronavirus Infections

A specific syllabus on nursing emergencies that will be fundamental for your professional development”
Advanced Master's Degree in Emergency Nursing in the Adult and Pediatric Patient
Care in critical situations such as accidents, heart attacks, respiratory failure or paralysis (among many other pathologies), represent a great challenge for healthcare personnel. Therefore, it is essential to have specialists with immediate reaction skills. At TECH Global University we have developed an Advanced Master's Degree in Emergency Nursing in the Adult and Pediatric Patient, with which you will learn the latest techniques and tools implemented in emergency care in this type of patient. The program has a 100% online study mode, focused on enhancing your skills progressively. Here, you will have state-of-the-art educational equipment, which includes the continuous accompaniment of a team of specialists and lessons supported by multimedia material. During the course of the two-year course, you will learn about nursing care in cardiac, respiratory, neurological, digestive, ophthalmological and endocrine emergencies, as well as traumatic accidents, osteoarticular injuries and infectious diseases such as coronavirus. By taking each thematic axis, you will obtain a high-level background to attend hospital and out-of-hospital emergencies with greater safety.
Be an expert in pediatric and adult patient emergency care.
According to reports published by the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 100 children die every hour worldwide due to accidents such as drowning, burns, falls or poisoning. They also indicated that non-communicable diseases, stroke and ischemic heart disease (among others) are the main causes of death in adults. This is why the specialization of professionals in this field is so essential. In this TECH postgraduate course you will find the necessary tools to strengthen your skills in the diagnosis and treatment of patients who require priority attention. By accessing our Postgraduate Certificate, you will contribute to the improvement in the quality of life of the user, through the implementation of the best Nursing services. During the course of the Professional Master's Degree, you will specialize in managing the organization of the hospital emergency unit, life support techniques and advanced cardiopulmonary resuscitation maneuvers. You will also master the preparation of sedoanalgesia, personalized pharmacology and diagnostic-therapeutic techniques. Because of this, you will be able to perform follow-ups and evaluations that contribute to the integral recovery of each patient.







