University certificate
The world's largest faculty of medicine”
Why study at TECH?
An intensive Postgraduate diploma in Management of Inflammatory Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases that will give you the keys to an innovative and comprehensive intervention"
Childhood is not safe from rheumatologic disease (RD). Although it is difficult to know their exact prevalence, given the absence of specific and global studies, they are potentially serious diseases that lead to a significant decrease in the quality of life of the affected child. Comprehensive care for patients and their families as a fundamental part of the process is an essential condition in the approach to this group of diseases.
This Postgraduate diploma offers a different look at the global care that the child affected by RD needs. A comprehensive approach that covers all aspects of this care: from pre- and post-diagnostic care to families, pharmacological criteria and psychological and emotional care for the affected person and their environment.
During this comprehensive program, professionals will have the opportunity to acquire the basic knowledge necessary to deal with the situations that arise around a child or adolescent suspected of having RMD. From the moment of diagnosis, with the development of the guidelines that the specialist must follow, to the information on procedures or attitudes to be avoided in this medical practice.
This is a 100% online program, nurtured and enriched with first-hand audiovisual material, created specifically by specialists in the field. It should be noted that, as it is a digital format, the professional will not have to move to a face-to-face center, and will be able to adapt their classes to the schedule that best suits them.
All aspects of the practice of Pediatric Rheumatology, with a global vision of the care of the affected patient, in the most complete Postgraduate diploma on the online teaching market”
This Postgraduate diploma in Management of Inflammatory Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases contains the most complete and up-to-date scientific program on the market. The most important features include:
- The latest technology in online teaching software
- A highly visual teaching system, supported by graphic and schematic contents that are easy to assimilate and understand
- Practical cases presented by practicing experts
- State-of-the-art interactive video systems
- Teaching supported by telepractice
- Continuous updating and recycling systems
- Autonomous learning: full compatibility with other occupations
- Practical exercises for self-assessment and learning verification
- Support groups and educational synergies: questions to the expert, debate and knowledge forums
- Communication with the teacher and individual reflection work
- Content that is accessible from any fixed or portable device with an Internet connection
- Supplementary documentation databases are permanently available, even after the program
The teachers of this Postgraduate diploma have been selected on the basis of two fundamental criteria: their proven experience and knowledge of RD in pediatrics and their proven teaching skills"
The program’s teaching staff includes professionals from the field who contribute their work experience to this educational program, as well as renowned specialists from leading societies and prestigious universities.
Its multimedia content, developed with the latest educational technology, will provide the professional with situated and contextual learning, i.e., a simulated environment that will provide an immersive education programmed to learn in real situations.
This program is designed around Problem-Based Learning, whereby the professional must try to solve the different professional practice situations that arise throughout the program. For this purpose, the professional will be assisted by an innovative interactive video system created by renowned and experienced experts.
With a methodological design based on proven teaching techniques, this Postgraduate diploma will take you through different teaching approaches to allow you to learn in a dynamic and effective way"
Our innovative telepractice concept will give you the opportunity to learn through an immersive experience, which will provide you with a faster integration and a much more realistic view of the contents: Learning from an expert"
Syllabus
The contents of this program have been developed by different specialists with a clear purpose: to ensure that our students acquire each and every one of the skills necessary to become true expert in this field. The content of this program will update the concepts in all aspects of the different disciplines involved in Inflammatory Pediatric rheumatology.
A comprehensive teaching program, structured in well-developed teaching units, oriented towards learning that is compatible with your personal and professional life"
Module 1. Attitude Towards Children with Suspected RMD
1.1. Medical History
1.1.1. Frequent Reasons for Consultation in Pediatric RMD
1.1.2. Family Background
1.1.3. Personal Background
1.1.4. Key Questions in RMD
1.1.5. Relevant Organs and Apparatus
1.1.6. Growth and Development
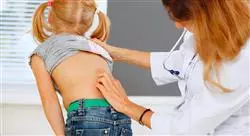
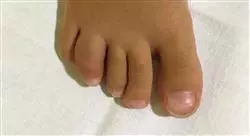
1.2. Exploration of the Locomotor System in Pediatric Rheumatology
1.2.1. Exploration of Upper Limbs
1.2.2. Exploration of Lower Limbs
1.2.3. Exploration of the Spine
1.2.4. Exploration of Gait
1.2.5. General Examination Adapted to Rheumatology
1.3. Complementary Tests
1.3.1. Image
1.3.1.1. Radiography
1.3.1.2. Ultrasound
1.3.1.3. Resonance
1.3.1.4. Others
1.3.2. Laboratory Tests
1.3.2.1. Blood Count:
1.3.2.2. Biochemistry
1.3.2.3. Reactants of the Acute Phase
1.3.2.4. Autoantibodies
1.3.2.5. Serology and Supplementation
1.3.2.6. Microbiology
1.3.2.7. Genetic Studies
1.3.2.8. Biomarkers
1.3.3. Study of Synovial Fluid
1.3.4. Clinical Neurophysiology
1.4. Multidisciplinary Assistance
1.4.1. What Does the Rheumatologist Do?
1.4.2. What Does the Pediatrician Do?
1.4.3. What Does the Nurse Do?
1.4.4. What Does the Psychologist Do?
1.4.5. What Does the Physiotherapist Do?
1.4.6. What Does the Occupational Therapist Do?
1.4.7. What Does the Social Worker Do?
Module 2. Musculoskeletal Alterations
2.1. Inflammatory Joint Pathology
2.1.1. Monoarthritis
2.1.1.1. Most Frequent Causes
2.1.1.2. Diagnostic Attitude
2.1.1.3. Therapeutic Approach
2.1.2. Oligoarthritis
2.1.2.1. Most Frequent Causes
2.1.2.2. Diagnostic Attitude
2.1.2.3. Therapeutic Approach
2.1.3. Polyarthritis
2.1.3.1. Most Frequent Causes
2.1.3.2. Diagnostic Attitude
2.1.3.3. Therapeutic Approach
2.2. Inflammation of the Entheses
2.2.1. Most Frequent Causes
2.2.2. Diagnostic Attitude
2.2.3. Therapeutic Approach
2.3. Muscular Pathology
2.3.1. Inflammatory Myopathies
2.3.2. Non-Inflammatory Myopathies
Module 3. Systemic Inflammation
3.1. Systemic Manifestations of Inflammation
3.1.1. Fever
3.1.2. Constitutional Syndrome
3.1.3. Fatigue
3.2. Alterations of the Eye with Rheumatologic Significance
3.2.1. Anterior Uveitis
3.2.2. Intermediate Uveitis
3.2.3. Posterior Uveitis
3.2.4. Epiescleritis
3.2.5. Refractive Defects
3.3. Cutaneous Alterations with Rheumatologic Significance
3.3.1. Psoriasis
3.3.2. Lesions Suggestive of Connective Tissue Disease
3.3.3. Lesions Suggestive of Autoinflammatory Disease
3.4. Digestive Alterations with Rheumatologic Significance
3.4.1. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
3.4.2. Complications of Malnutrition and Malabsorption
3.5. Cardiopulmonary, Neurological and Renal Alterations
3.5.1. Cardiopulmonary Disorders
3.5.2. Neurological Alterations:
3.5.3. Renal Disorders
Module 4. Pharmacological Treatment in Pediatric Rheumatology
4.1. Symptomatic Treatment
4.1.1. Analgesics
4.1.2. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
4.1.3. Opioids
4.1.4. Antiepileptics
4.1.5. Antidepressants
4.2. Directed Treatment
4.2.1. Disease-Modifying Drugs
4.2.2. Biological Evidence
4.2.3. Biosimilars
4.2.4. Small Molecules
Module 5. Other Musculoskeletal Symptoms
5.1. Exercise and Physical Activity in Children
5.1.1. Exercise, Physical Activity and Sport
5.1.2. Specifics of Exercise in Children with RMD
5.2. Rehabilitation
5.2.1. Splints and Orthoses
5.2.2. Physical Therapies in Children
5.3. Orthopedic Surgery
5.3.1. Special Features of Immature Bone and the Growing Skeleton
5.3.2. Infantile Fractures
5.3.2.1. Most Common Traumatic Fractures and Traumatic Epiphysiolysis
5.3.2.2. Common Techniques of Osteosynthesis in Children
5.3.3. Infection Management in the Locomotor System in Children
5.3.4. Surgery of Growing Spine Deformities
5.3.5. Osteotomies of the Pelvis and the Upper Extremity of the Femur
5.4. Nutritional Advice
5.4.1. Obesity
5.4.2. Malnutrition
5.4.3. Supplements
5.5. Psychological Approach to Pediatric RMDs
5.5.1. Fears, Phobias and Anxieties
5.5.2. Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Panic Disorder
5.5.3. Depression in Childhood and Adolescence
5.5.4. Sleep Disorders
5.5.5. Eating Disorders
5.5.6. Dissocial Disorder
5.5.7. Learning Disorders
5.5.8. Training of Parents of Children with RMD
5.5.9. Family Behavioral Intervention
5.6. Occupational Intervention
5.6.1. Occupational Schedules
5.6.2. Play as Therapy
5.6.3. Technical Aids
5.7. What Not to Do?
Module 6. Pharmacological Treatment in Pediatric Rheumatology
6.1. Vaccines
6.1.1. Official Vaccination - Peculiarities to Be Taken into Consideration
6.1.2. Extra Vaccination According to Diseases and Treatments
6.2. Chemoprophylaxis
6.2.1. What to Do in the Event of Surgery?
6.2.2. What to Do in the Event of Intercurrent Infections?
6.3. Tuberculosis Screening
6.3.1. Who Should Be Screened?
6.3.2. Existing Tests
6.3.3. What to Do in Case of a Positive Test?
6.4. Osteoporosis Screening in Children
6.4.1. Who Should Be Screened?
6.4.2. Existing Tests
6.4.3. What to Do in Case of a Positive Test?
Module 7. "Wiki” of Diseases (Resources to Which All Modules Address)
7.1. Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
7.1.1. Uveitis Associated with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
7.1.2. Macrophage Activation Syndrome
7.2. Vasculitis
7.2.1. Schönlein-Henoch Purpura
7.2.2. Kawasaki Disease
7.2.3. Wegener's Granulomatosis, Takayasu's Arteritis, Churg-Strauss Syndrome, and Other Vasculitides
7.3. Connectivopathies
7.3.1. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
7.3.2. Sjögren's Syndrome
7.3.3. MCD
7.3.4. Antiphospholipid Syndrome
7.3.5. Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy
7.3.5.1. Juvenile Dermatomyositis
7.3.6. Scleroderma
7.3.6.1. Localized Scleroderma
7.3.6.2. Systemic Sclerosis
7.4. Autoinflammatory Syndromes
7.4.1. PFAPA Syndrome
7.4.2. Inherited Relapsing Fever Syndromes
7.4.3. Other Autoinflammatory Syndromes
7.5. Osteoarticular Infections
A unique, key and decisive training experience to boost your professional development"
Postgraduate Diploma in Management of Inflammatory Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases
Management of pediatric inflammatory rheumatic diseases refers to treatment and care strategies for children with chronic inflammatory disorders of the musculoskeletal system, such as juvenile idiopathic arthritis and juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus. management of pediatric inflammatory rheumatic diseases is a multidisciplinary approach that aims to reduce symptoms, improve musculoskeletal function, and promote quality of life for affected children. This management involves a combination of medications, physical and occupational therapy, regular monitoring, and patient and family education for home authoring.
The management of these diseases involves a multidisciplinary approach involving specialists in pediatrics, rheumatology, gastroenterology, ophthalmology, psychiatry, physical and occupational therapy. The primary goal of management is to reduce the pain, inflammation and disability associated with these diseases, ensure proper joint function and improve the quality of life of affected children.
Treatment may include the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids, biologic therapies and immunomodulators, as well as physical and occupational therapy to improve mobility and muscle function. Diet and physical activity are also important in promoting bone and muscle health.
It is important to conduct regular monitoring of the disease in order to detect any complications or changes in the child's health status and make treatment adjustments accordingly. Management strategies should also include patient and family education to help them understand the disease and manage symptoms at home.
Thisonline educational program seeks to provide students with comprehensive education that is complete enough for participants to acquire solid knowledge and skills in the management of these disorders in children. In addition, to practical elements, such as clinical cases and discussion of real clinical situations, so that students can apply theoretical knowledge in practical situations.